In the business world, efficiency and quality are two interrelated factors. Good products and services alone will not be enough if the processes supporting them are still full of errors or inconsistencies. This is where the importance of the Six Sigma method lies, a proven approach to balancing quality improvement while reducing costs.
Six Sigma is not only used by large companies but has also been applied across industries worldwide. However, to truly understand how this method works, it is important to get deeper insight into what Six Sigma is, what principles underlie it, and how its implementation can have a real impact on business. Here is the complete guide!
What Is Six Sigma?

Six Sigma was first developed by Motorola in the 1980s and later popularized by General Electric (GE) as a strategy for improving quality management.
The name “Six Sigma” itself comes from a statistical term, namely the standard deviation recognized to describe how consistently a process can run. At highest level (six sigma), quality can considered almost perfect with only 3.4 defects per one million opportunities. This high standard has now become a symbol of companies’ efforts to achieve truly reliable quality.
Six Sigma is a data-driven framework that combines statistical principles, process management, and continuous improvement. This method focuses on using data and statistical analysis to detect and reduce defects while increasing consistency in business performance. The essence is not only to reduce the error rate but also to ensure that every step runs efficiently, consistently, adaptively, and is sustainable against change.
Furthermore, Six Sigma is a mindset framework that emphasizes the importance of data-based decision making, not merely intuition. Because of its flexible and cross-functional nature, this method is now relevant not only to manufacturing but also to various sectors such as services, customer support, supply chains, and even non-profit organizations seeking to improve operational quality.
Discover More : Smart Ways to Delegate Tasks to Improve Team Performance
Principles of Six Sigma (DMAIC)
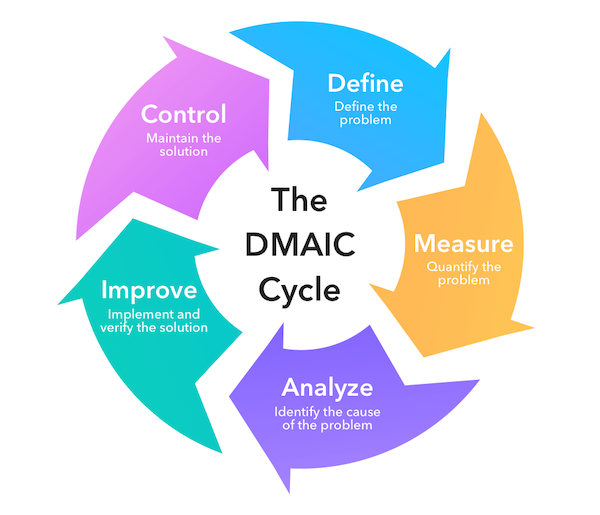
The main principle of Six Sigma comes from the DMAIC framework (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control). These stages serve as a systematic guide for companies that want to solve problems and continuously improve processes.
Define
The process begins with the Define stage, where the company tries to define the problem, project scope, and objectives to be achieved. At this stage, the company must ensure whether the chosen issue is truly important and relevant to customer needs as well as business strategy.
Measure
The next stage is Measure. As the word suggests, this is the process of collecting data to deeply understand the actual condition of the process. This data serves as an objective basis, so the team does not only assume but truly observes how performance is running.
Analyze
Once the data has been collected, the Analyze stage begins. As the name suggests, here the company conducts in-depth analysis to find the root cause of the problem. With the right analysis, companies can avoid misguided handling and focus on solutions that address the source of the issue.
Improve
The next step is Improve, which means selecting and enhancing corrective solutions. At this stage, the team chooses ideas based on their effectiveness in addressing the root cause. After testing, they gradually implement the best idea to keep risks under control.
Control
The final step, which is no less important, is Control. In this phase, company ensures that improvements can sustained in the long term. This done by creating new standards for the company, preparing appropriate SOPs, or setting up monitoring systems. In this way, success will not only be temporary but will truly become part of the organizational culture.
Benefits of Six Sigma for Operations

In terms of operations, Six Sigma provides enormous benefits because it directly relates to the core of a company’s daily activities. This method greatly helps organizations reduce process variations that do not add value, so production and service stages can run more effectively.
In addition, this method also drives workflow efficiency. Through data-based analysis, companies can detect waste points such as unnecessary waiting times, duplicate processes, or excessive use of resources. Improvements in these areas will directly impact operational cost savings and increased team productivity.
The application of Six Sigma also improves timeliness in operations. For example, in a service focused on product delivery, companies can cut delivery times because workflows are designed with minimal obstacles. This results in faster service, which ultimately strengthens customer satisfaction.
In other words, Six Sigma is highly beneficial for business operations. It not only makes processes faster and cheaper but also more reliable and, most importantly, customer-oriented.
Discover More : Effective Ways to Become a Reliable and Qualified Leader: Roles and Challenges
Certification and Real-World Implementation

To gain a more comprehensive understanding of the Six Sigma method, professional certification is one of the most recognized paths. This certification has several levels, ranging from White Belt for a basic understanding of the Six Sigma method, Yellow Belt for involvement in small-scale improvement projects, Green Belt for roles in data analysis and project management, to Black Belt responsible for leading major initiatives and training team members. At the highest level is the Master Black Belt, which acts as a strategic advisor and methodology developer within the organization.
This certification not only provides professional recognition but also enhances credibility and sharpens practical skills in using statistical tools, managing change, and integrating Six Sigma with business strategy. Companies with Six Sigma-certified employees are potentially better prepared to carry out process improvement projects effectively and consistently.
General Electric (GE) on Six Sigma

In practice, one of the most impactful examples of Six Sigma implementation can be seen at General Electric (GE) under the leadership of Jack Welch in the 1990s. GE implemented Six Sigma across almost all business lines, from manufacturing to customer service. The results were extraordinary: GE recorded billions of dollars in cost savings while simultaneously improving product quality and customer satisfaction. This success made Six Sigma more popular and widely adopted across various industries, including banking, healthcare, and services.
At GE itself, the Six Sigma transformation began with top-level commitment. The CEO required each business unit to run projects with clear financial targets. Key managers and staff trained step by step (Green/Black Belt), then worked on high-priority projects directly addressing critical-to-quality elements for customers.
First, the team collected baseline performance data and analyzed root causes using DMAIC. They then tested solutions on a small scale before standardizing them through new SOPs and tollgate reviews. Finally, they developed new product designs with Design for Six Sigma, ensuring that the team built quality into the process from the start.
Thus, Six Sigma is not just a method but a framework capable of guiding companies toward higher quality standards while ensuring sustainable cost efficiency. With proper implementation, organizations can reduce defects, improve processes, and create more consistent customer satisfaction.
If your company wants to improve quality while enhancing operational efficiency through a structured approach, Arghajata Consulting is ready to be your partner in designing and implementing Six Sigma according to your business needs. Contact us today and start your journey toward superior and competitive business processes.


















